Black American women with low levels of vitamin D have higher odds of developing colon cancer, according to new research that echoes previous findings in white women.
Researchers used a vitamin D prediction model for nearly 50,000 participants in the Black Women's Health Study and concluded that those with predicted levels in the bottom 25% had an estimated 40% higher risk of colon cancer than those in the top 25%.
The study was recently published online in the journal Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.
"Our findings, taken together with established evidence that vitamin D levels are generally lower in the Black population than other groups, suggest that low vitamin D may contribute to disproportionately high colorectal cancer incidence among Black [people]," study author Julie Palmer says in a Boston University news release.
Yes Or No: Does Red Meat Cause Colon Cancer?
The link between vitamin D and colon cancer
Palmer and her team say it's important to determine if there is a link so Black people who may have an increased risk for developing colon cancer can boost their vitamin D levels.
Vitamin D is involved in many processes in the body and has been shown to have anti-cancer properties. Black people tend to have lower levels because sunlight is the major source of vitamin D aside from taking vitamin supplements, according to authors.
They also note that Black Americans have the highest rates of colon cancer incidence and death. More than 150,000 people in the United States a year are diagnosed with it, making colon cancer the third most common cancer in both men and women excluding skin cancer, according to the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
How much vitamin D is required?
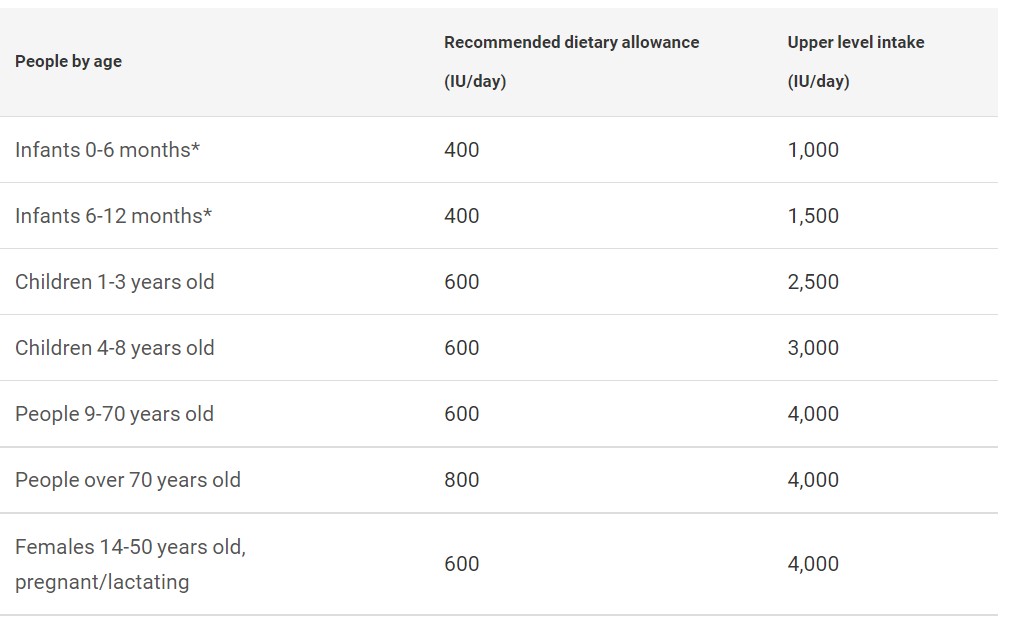
There is a debate around how much vitamin D the body needs.
Approximately 600-4,000 IU is considered a safe daily dose for adults to maintain healthy levels of vitamin D. However if your current levels
are low or you have had low exposure to the sun; you may need larger doses.
The optimal blood level of vitamin D also doesn't have a concrete number, but usually falls between 20 and 50 ng/ml.
How to increase your vitamin D
You can naturally increase your vitamin D in the following ways:
1. Sunlight

Getting natural sunlight is the old-fashioned way to get vitamin D. Our skin hosts a type of cholesterol that makes vitamin D in the presence of sunlight. Exactly how much vitamin D your body produces depends on your skin tone, the exposed part of the body, age, etc. Aim for 10-30 minutes of sunlight several times per week. If you have darker skin, you may need a bit more sunlight. Just be sure that you protect your skin and use sunscreen.
2. Seafood
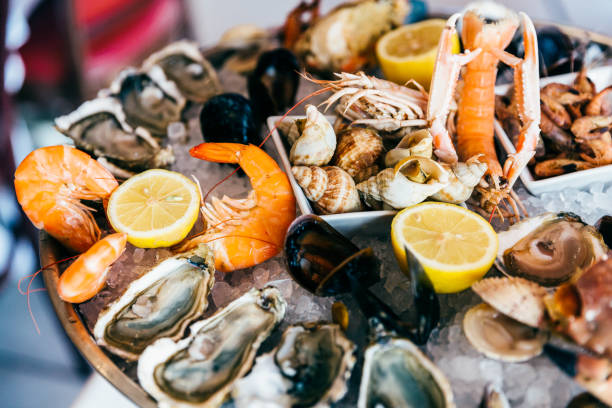

Fatty fish and seafood are some of the most natural food sources of vitamin D. For an added bonus try tuna, rainbow trout, mackerel, oysters, salmons, sardines, and anchovies. They are also rich in heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids.
3. Mushrooms
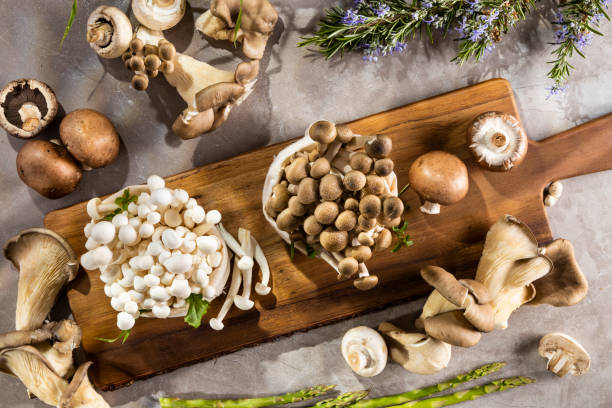

Mushrooms are the only completely plant-based option for vitamin D as they make their vitamin D upon exposure to sunlight just like humans. Humans produce a form of vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) and mushrooms produce D2 (ergocalciferol). Shitake mushrooms are highly recommended for vitamin D, just be sure to buy them from a trusted supplier such as the farmer's market to avoid exposure to poisonous varieties.
RELATED: What Your Bowels Say About Your Health
4. Egg yolks
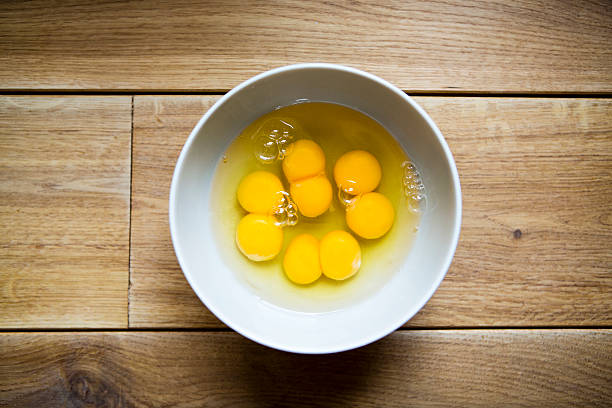

Egg yolks are a common source of vitamin D and an easier way to add it to your diet.
5. Fortified foods

Fortification involves adding vitamin D to certain foods to increase their nutritive value.
These foods include:
- soy, almond, and hemp milk
- orange juice
- ready-to-eat cereals
- certain types of yogurt
- tofu
6. Dairy foods

Swiss cheese, cow milk, curds and cottage cheese are also good Vitamin D sources.
7. Cod liver oil

Just one tablespoon of cod liver oil contains 1360 international units of vitamin D. Try taking it with warm water or in capsule form to enhance your vitamin D levels.
8. Supplements

Taking supplements may be the best way to ensure that you are getting an adequate amount of vitamin D, especially if your numbers are extremely low.
Vitamin D exists in two forms:
- D2 (ergocalciferol): Comes from plants
- D3 (cholecalciferol): Comes from animals
Research suggests that D3 may be more effective in raising and maintaining vitamin D levels.
When purchasing vitamin D supplements, be sure to purchase high-quality supplements that have been independently tested.
Don’t ASSume: Why Colon Cancer Is Killing More Black People
9. Ultraviolet UV lamp
UV radiation has widely been used as a therapeutic for various skin conditions. However, recently it has been suggested to be great at raising vitamin D levels as well. UV lights can mimic the sun and be helpful if you have limited sun exposure. Be careful when using UV lamps. Too much exposure can burn your skin. It is recommended that you limit exposure to no more than 15 minutes at a time.
10. Exercise

Regular physical activity such as walking, jogging or cycling can increase your vitamin D levels. For an added bonus, try doing them in the sun whenever possible.
Having an adequate amount of vitamin D is essential to how we function on a daily. The following are symptoms of low vitamin D that you should watch out for:
- Nausea
- Increased thirst and urination
- Poor appetite
- Constipation
- Weakness
- Confusion
- Ataxia (a neurological condition that may cause slurring and stumbling of words)
If you experience any of these symptoms, contact your doctor. They can run blood tests to confirm that you have low vitamin D and help you determine your next steps.