A rare, but highly contagious form of ringworm that can spread via sexual contact has been spotted in the U.S. for the first time.
Ringworm, also known as tinea, is a skin infection caused by a variety of fungi. In this case, a fungus is the culprit. It’s previously been documented in Southeast Asia and in Europe. For example, in 2023, Paris-based doctors published a case series of 13 infections documented among men in the city. Where those recent cases took place highly suggest that the fungus might currently be circulating within that demographic, although anyone can develop the infection.
Now, in a paper published in June 2024 in JAMA Dermatology, doctors in New York City have reported what they believe to be the first U.S. case of the infection.
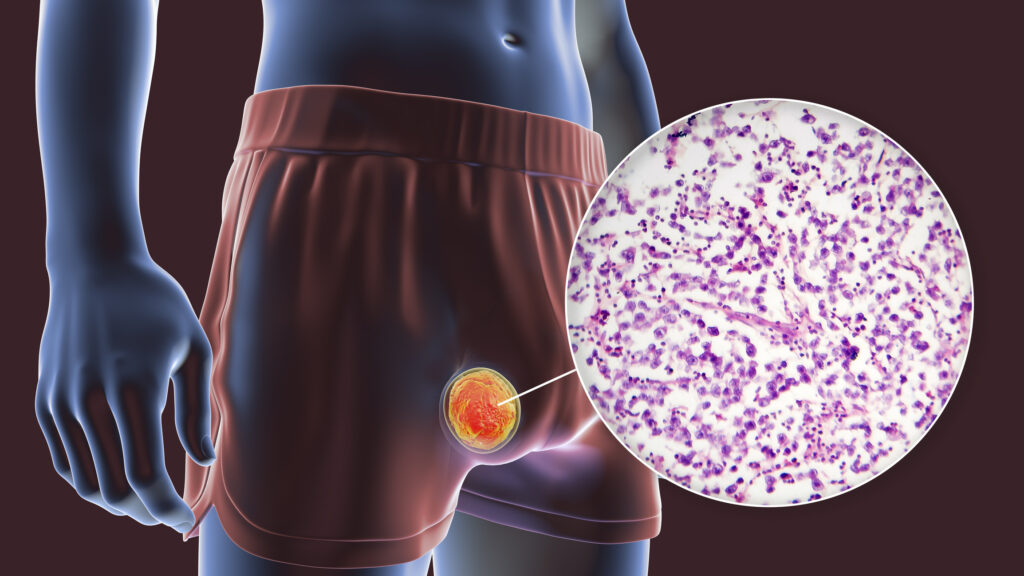
The new case involves a New York City native man in his 30s who reported having sex with multiple men during a trip to England, Greece and California. When he got home, he developed a red, itchy rash on his legs and across his groin and buttocks.
Tests revealed he had a sexually transmitted fungus, called Trichophyton mentagrophytes type VII (TMVII). It is the first time the fungus has been identified in the U.S. Last year, doctors in France reported 13 such cases. Twelve of those patients were men who have sex with men.
The man’s infection responded to standard anti-fungal medications but ultimately took four and a half months to heal fully.
He was put on fluconazole for four weeks without improvement, then six weeks of terbinafine and approximately eight additional weeks of itraconazole. All are oral anti-fungals.
“Healthcare providers should be aware that Trichophyton mentagrophytes type VII is the latest in a group of severe skin infections to have now reached the United States,” said study lead author and dermatologist Avrom S. Caplan, MD. Dr. Caplan is an assistant professor in the Ronald O. Perelman Department of Dermatology at NYU Grossman School of Medicine.
What to Look for and How to Stay Safe
“Dermatologists in the U.S. should be aware of [Trichophyton mentagrophytes] infections,” the authors said in the report. “Prompt treatment may reduce the risk for scarring and transmission.”
It is also important that patients are open with their physicians about new or persistent rashes in their genital area, as well as their sexual history where relevant.
“Since patients are often reluctant to discuss genital problems, physicians need to directly ask about rashes around the groin and buttocks, especially for those who are sexually active, have recently traveled abroad, and report itchy areas elsewhere on the body,” senior study author Dr. John Zampella, an associate professor of dermatology at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine, said in a statement.
Symptoms of TMVII are similar to those associated with ringworm — mainly itchy, round, scaly patches on the skin. Highly inflammatory lesions and abscesses may also be seen.
Researchers caution that TMVII rashes differ from the classic circular expression of ringworm and may be confused for eczema, delaying proper treatment.
Infections caused by TMVII are difficult to treat and can take months to clear up, but thus far, appear responsive to standard antifungal therapies.
TMVII had been found among men having contact with sex workers in Southeast Asia and has reached Europe, where evidence suggests it is spread through sexual contact.
Contrary to prior reports, shaving the groin and intimate area did not increase the likelihood of contracting TMVII.
Last year, 13 instances of TMVII were recorded in France. Of the diagnosed, 11 men reported sex exclusively with men and nine disclosed having multiple partners in the month preceding infection.
Other Types of Fungal Infections
The most common type of fungal infection is called Thrush.
Your chance of developing genital fungal infections may be increased:
- by taking antibiotics
- from restricted airflow to the genitals by wearing tight underwear/clothes or synthetic fabrics
- by vaginal douching (washing) with perfumed bath products
- if you have diabetes or are pregnant
And for men:
- from not washing under the foreskin
Some fungal infections can be passed on sexually – these include Thrush, Jock Itch (like athlete’s foot, but around the genitals), and Balanitis (inflammation of the end of the penis).
Dr. Caplan adds that he plans to work with leading fungi experts around the United States and internationally over the next few months to expand research efforts and track emerging cases.