The sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) or sexually transmitted infections (STIs) most people know and would think of as common is gonorrhea, chlamydia, or even HIV. But there is one sexually transmitted disease that is common, but people never talk about it like they should. It's called Trichomoniasis.
I can hear it now: "Tric o-what?"
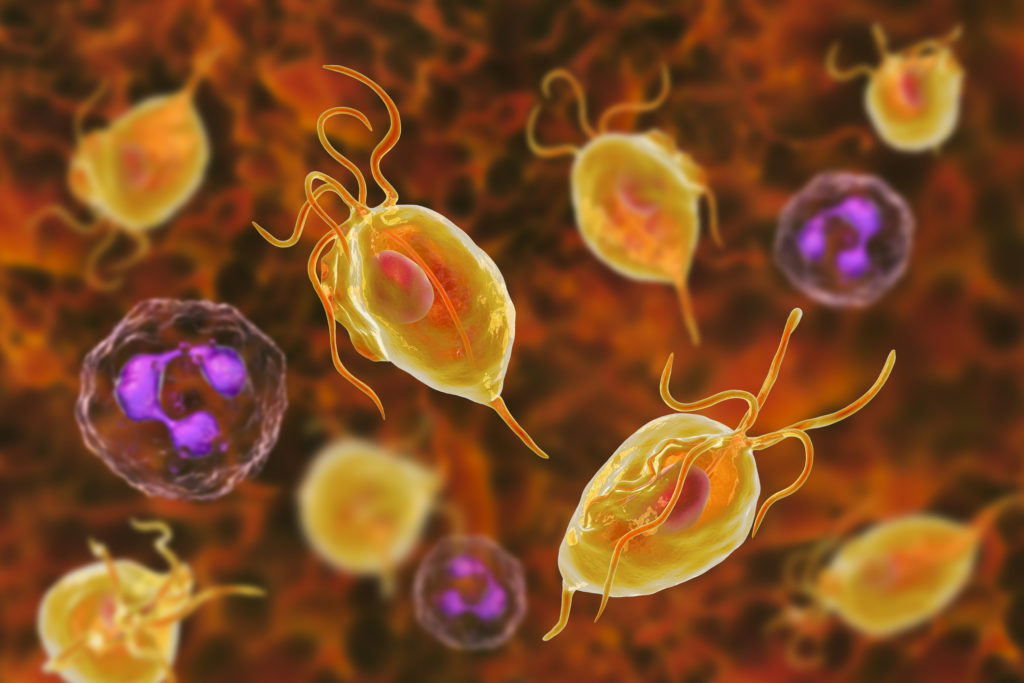
Trichomoniasis is caused by a parasite called trichomonas vaginalis, a type of single-celled organism (or protozoon).
In women, trichomoniasis can cause a foul-smelling vaginal discharge, genital itching, and painful urination. Pregnant women who have trichomoniasis might be at higher risk of delivering their babies prematurely.
That said, there's a lot we don't know about trichomoniasis—and not a lot is being done to stem its spread. Even though trichomoniasis is common, it's not a reportable disease, which means that local and state health departments and the CDC don't require new cases to be reported when they're diagnosed.
This also means that public health programs aren't putting as much effort into tracking or controlling its transmission as they might with other STIs.
As a matter of fact, Trichomoniasis (or "Trich") is the most common curable STD. In the United States, CDC estimates that there were more than two million trichomoniasis infections in 2018. However, only about 30% develop any symptoms of trichomoniasis. Infection is more common in women than in men.
Older women are more likely than younger women to have been infected with trichomoniasis.
Symptoms
Many women and most men with trichomoniasis have no symptoms, at least not at first. Trichomoniasis signs and symptoms for women include:
- An often foul-smelling vaginal discharge — which might be white, gray, yellow, or green
- Genital redness, burning, and itching
- Pain with urination or sexual intercourse
Trichomoniasis rarely causes symptoms in men. When men do have signs and symptoms, however, they might include:
- Irritation inside the penis
- Burning with urination or after ejaculation
- Discharge from the penis
Causes
The parasite passes from an infected person to an uninfected person during sex. In women, the most commonly infected part of the body is the lower genital tract (vulva, vagina, cervix, or urethra). In men, the most commonly infected body part is the inside of the penis (urethra).
During sex, the parasite usually spreads from a penis to a vagina, or from a vagina to a penis.
It can also spread from one vagina to another vagina. It is not common for the parasite to infect other body parts, like the hands, mouth, or anus. It is unclear why some people with the infection get symptoms while others do not. It probably depends on factors like a person’s age and overall health. Infected people without symptoms can still pass the infection on to others.
What To Do
According to The Mayo Clinic, to prevent reinfection with the organism that causes trichomoniasis, both partners should be treated. The most common treatment for trichomoniasis involves taking one megadose of metronidazole (Flagyl) or tinidazole (Tindamax). You can reduce your risk of infection by using condoms correctly every time you have sex.
For more information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases you can still get while using a condom, click here.