 Multiple sclerosis or MS is a disease that affects the brain and spinal cord, resulting in loss of muscle control, vision, balance, and sensation (such as numbness). With MS, the nerves of the brain and spinal cord are damaged by one’s own immune system. Thus, the condition is called an autoimmune disease.
Multiple sclerosis or MS is a disease that affects the brain and spinal cord, resulting in loss of muscle control, vision, balance, and sensation (such as numbness). With MS, the nerves of the brain and spinal cord are damaged by one’s own immune system. Thus, the condition is called an autoimmune disease.
Autoimmune diseases are those whereby the body’s immune system, which normally targets and destroys substances foreign to the body such as bacteria, mistakenly attacks normal tissues. In MS, the immune system attacks the brain and spinal cord, the two components of the central nervous system. Other autoimmune diseases include lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
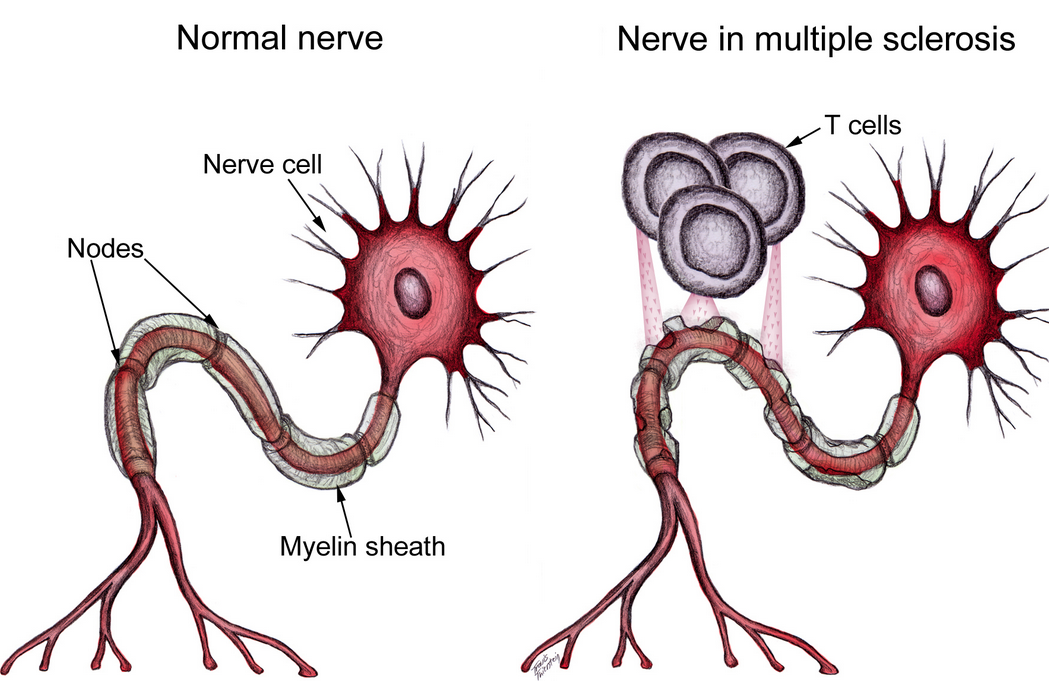
The central nervous system is made up of nerves that act as the body’s messenger system. Each nerve is covered by a fatty substance called myelin, which insulates the nerves and helps in the transmission of nerve impulses, or messages, between the brain and other parts of the body. These messages control muscle movements, such as walking and talking.
multiplesclerosis
MS gets its name from the buildup of scar tissue (sclerosis) in the brain and/or spinal cord. The scar tissue or plaques form when the protective and insulating myelin covering the nerves is destroyed, a process called demyelination. Without the myelin, electrical signals transmitted throughout the brain and spinal cord are disrupted or halted. The brain then becomes unable to send and to receive messages. It is this breakdown of communication that causes the symptoms of MS.
Although the nerves can regain myelin, this process is not fast enough to outpace the deterioration that occurs in MS. The types of symptoms, severity of symptoms, and the course of MS vary widely, partly due to the location of the scar tissue and the extent of demyelination.
According to the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, the condition affects approximately 400,000 Americans and is, with the exception of trauma, the most frequent cause of neurological disability beginning in early to middle adulthood.
MS is two to three times as common in females as in males and its occurrence is unusual before adolescence. A person has an increased risk of developing the disease from the teen years to age 50, with the risk gradually declining thereafter.







