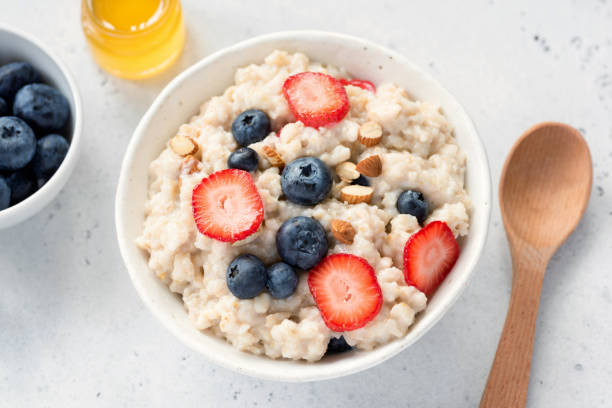
A key part of managing diabetes is being mindful of what you eat. That means it’s important to know which foods are best for you and when to have them. While oatmeal is generally considered a healthy option, does that mean it’s good for diabetics? Let’s find out.
Is Oatmeal A Carbohydrate?
Yes, oatmeal is a carbohydrate. However, it’s considered to be a high-fiber carbohydrate, which is an excellent alternative to other carbs that you might have for breakfast. The soluble fiber content in oats is known for helping with lowering blood glucose. Oatmeal also contains a limited quantity of natural sugars, though it will still affect your blood sugar level to some extent.
Is Oatmeal Good For Diabetics?
Oatmeal is typically considered to be good for diabetics because it can help them to manage the condition. While oatmeal is a carbohydrate, it’s also rich in other nutrients that can be helpful for someone with diabetes. These include fiber, protein, iron, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
The overall effect of these nutrients is that they have a positive impact on managing your blood sugar level. Of course, that depends on choosing the right kind of oatmeal.
It’s also important to note that the studies so far highlight the benefits of oatmeal for those who are prediabetic or have type 2 diabetes. Researchers have not yet established benefits for type 1 diabetes.
RELATED: 10 Delicious Diabetes-Friendly Breakfast Ideas
How Does Eating Oatmeal Help Diabetes And Blood Sugar?
The soluble fiber in oatmeal is what helps to regulate blood sugar levels. Oatmeal contains beta-glucan, which is a type of fiber that slows down digestion in the small intestine.
As a result, it will take longer for glucose to get into the bloodstream and your blood sugar levels are easier to manage. Additionally, oatmeal has a low glycemic index so it won’t have a high impact on your blood sugar level.
Benefits Of Oatmeal For Diabetics
- The high fiber content can help manage blood sugar levels. It can also lead to you feeling fuller once you’ve eaten so it can be great for weight management.
- Depending on how you use insulin to manage your diabetes, eating oatmeal can remove your need for a shot because you’re not eating your usual carbohydrate-rich breakfast.
- Oatmeal is known to lower your cholesterol levels as well so it’s a heart-healthy option for diabetics. This is good because diabetes can affect the heart.
- There is also evidence that oatmeal has anti-inflammatory properties that can be helpful for people with diabetes. That’s because inflammation in the body has been shown to make chronic illnesses like diabetes worse.
Which Oatmeal Is Best For People Living With Diabetes?
Currently, there are three forms of oatmeal available on the market - steel-cut, rolled, and instant. The best oatmeal for those who are living with diabetes is the one that’s the least processed and has the lowest glycemic index.
With that in mind, you should opt for steel-cut oatmeal. This type of oatmeal is not heavily processed so it retains a lot of its nutrients - especially the soluble fiber that you need to manage diabetes well.
Rolled oats are more processed and also have a higher glycemic index. You should definitely avoid instant oatmeal as it has lower nutrient content with the highest glycemic index.
RELATED: Perfect Steel Cut Oatmeal
How To Prepare Oats For Diabetic Patients
When preparing oatmeal for those who are diabetic, it’s a good idea to use water, unsweetened soy milk, or low-fat milk. A little nut butter can serve as added protein.
You can also add a little cinnamon, almonds, walnuts, or fresh berries for taste without affecting the sugar content too much. If you’re going to use sweeteners, cream, or dried fruits, it’s important not to use too much as it’s easy for the sugars to climb out of control. Common sweeteners include honey, brown sugar, and syrup but these can all cause your blood sugar to spike.
Final Words On Oatmeal And Diabetes
It’s generally accepted that oatmeal is good for people who have diabetes. However, you have to choose steel-cut oats and prepare them in a way that doesn’t add too much sugar. Since oatmeal might not be right for everyone, however, it’s a good idea to talk to your doctor before making it a regular part of your diet.