Cardiac arrest is a serious medical emergency that occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating. While it often seems to strike without warning, research suggests that there may be subtle signs that could serve as potential warnings the day before an event. Paying attention to these signs and taking appropriate action could potentially save lives.
Cardiac arrest warning signs
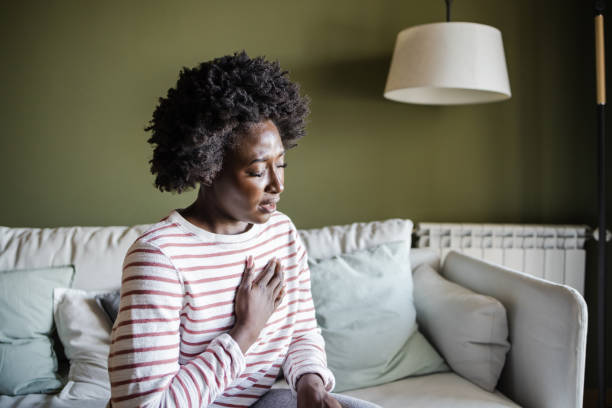
Fully 50% of people who experienced a sudden cardiac arrest had a telling symptom 24 hours before, and these symptoms are different in men than women, a new study suggests. For women, the most prominent symptom of an impending sudden cardiac arrest is shortness of breath; for men, it is chest pain and pressure.
“Yes, warning symptoms are associated with cardiac arrest, and these symptoms are sex-specific,” says study author Dr. Sumeet Chugh. He is the chair in cardiac electrophysiology research and medical director of the Heart Rhythm Center in the department of cardiology at the Smidt Heart Institute of Cedars-Sinai in Los Angeles.
It’s been thought that cardiac arrest comes on without warning, which is why the overwhelming majority of people who experience it outside of a hospital die within minutes, but that may not be the case and identifying any warning signs can give folks a fighting chance, Chugh adds.
When the researchers reviewed data from two community-based studies of people who experienced sudden cardiac arrest and compared their symptoms to those in people who sought emergency care but didn’t experience cardiac arrest, they found that 50% of people who had a sudden cardiac arrest experienced at least one telltale symptom the day before, namely chest pain in men and shortness of breath in women.
What’s more, smaller groups of men and women experienced palpitations, seizure-like activity and flu-like symptoms before they suffered cardiac arrest. One study took place in Ventura, Calif., and the other took place in Portland, Ore. And both yielded similar results.
Still, Chugh cautions that chest pain and shortness of breath can occur for other reasons and don’t necessarily mean a person is on the verge of cardiac arrest. However, when these occur in someone who also has high blood pressure, diabetes or underlying heart disease, they are more likely to be associated with cardiac arrest. In the future, apps or smart watches may further narrow down who is most at risk for sudden cardiac arrest, Chugh notes.
“We have to combine other features with warning symptoms to help people understand if they are likely experiencing a cardiac arrest and need help right away,” Chugh says.
Heeding any warning signs of cardiac arrest may help save a person’s life, according to Dr. Raman Mitra, director of the electrophysiology laboratory at North Shore University Hospital in Manhasset, N.Y.
“We think of sudden cardiac arrest as a person being perfectly fine and then collapsing, but there may be a way that we can identify these people earlier so that help can be alerted,” Mitra says. “If chest pain is new and associated with shortness of breath, heart palpitations, dizziness, passing out, sweating or nausea, seek medical attention.”
To make it easy to remember:
Sudden Symptoms
Symptoms of sudden cardiac arrest are immediate and severe and include:
- Sudden collapse.
- No pulse.
- No breathing.
- Loss of consciousness.
Pre-Symptoms of Cardiac Arrest
Sometimes other symptoms occur before sudden cardiac arrest. These might include:
- Chest discomfort.
- Shortness of breath.
- Weakness.
- Fast-beating, fluttering or pounding heart called palpitations.
RELATED: How To Dramatically Boost Survival of Cardiac Arrest
What causes cardiac arrest?
Typically caused by heart rhythm abnormalities, cardiac arrest occurs when the heart stops pumping. When this happens,