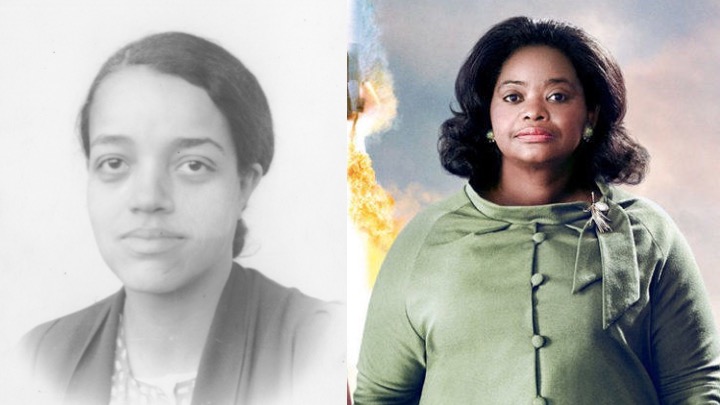
Dorothy Vaughan, one of the hidden figures in American space history that has long been swept under the rug is now out in the open and being told in the blockbuster movie, Hidden Figures, starring Taraji P. Henson and Janelle Monae as the unsung Black women who were instrumental in getting the first men on the moon. Dorothy is played by award-winning actress, Octavia Spencer.
Those who speak of NASA's pioneers rarely mention the name Dorothy Vaughan, but as the head of the NACA's segregated West Area Computing Unit, Vaughan was both a respected mathematician and NASA's first African-American manager.
As a college graduate and a teacher, Dorothy stood near the top of what most Negro women could hope to achieve. Teachers were considered the “upper level of training and intelligence in the race,” a ground force of educators who would not just impart book learning but live in the Negro community and “direct its thoughts and head its social movements.” She had earned a full-tuition scholarship to Wilberforce University, the country’s old private Negro college, in Xenia, Ohio. At Wilberforce, Dorothy earned “splendid grades” and chose math as her major. When she was an upperclassman, one of Dorothy’s professors at Wilberforce recommended her for graduate study in mathematics at Howard University, in what would be the inaugural class for a master’s degree in the subject.
But since the family's money was low, she opted to earn a degree in education and pursue teaching, the most stable career for a black woman with a college degree.
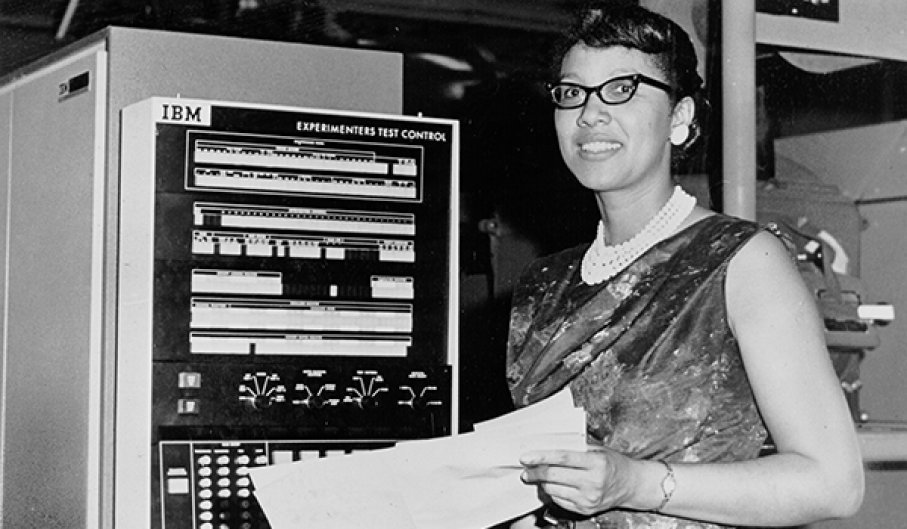

In the first week of May 1943, the Norfolk Journal and Guide published an article that would call to Dorothy like a signpost for the road not taken. “Paving the Way for Women Engineers,” read the headline. The accompanying photo showed 11 well-dressed Negro women in front of Hampton Institute’s Bemis Laboratory, graduates of Engineering for Women, a war training class.
So that spring, Dorothy Vaughan carefully filled out and mailed two job applications: one to work at Camp Pickett, where the need for labor was so great, so undifferentiated, that there was virtually no possibility that they would not hire her. The other, much longer application reviewed her qualifications in detail. Work history. Personal references. Schools attended: high school and college. Courses taken, grades received. Languages spoken (French). Foreign travels (none). Would you be willing to accept a position abroad? (No.) Would you be willing to accept a position in Washington, D.C.? (Yes.) How soon could you be ready to start work? She knew the answer before her fingers carved it into the blank: Forty-eight hours, she wrote. I can be ready to go within 48 hours.
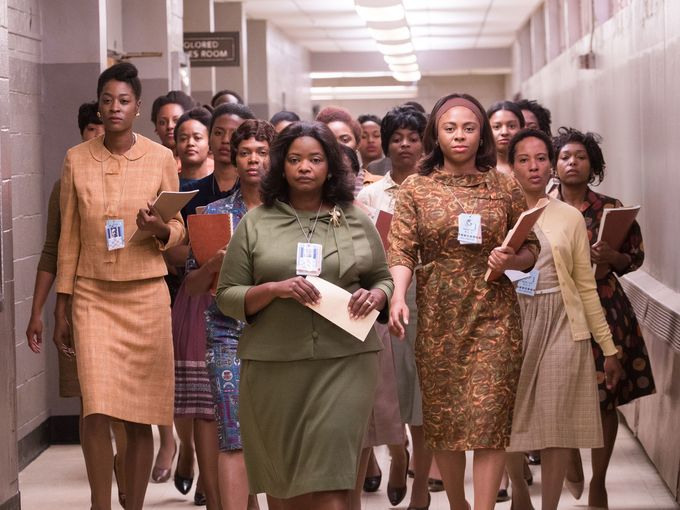

Dorothy Vaughan came to the Langley Memorial Aeronautical Laboratory in 1943, during the height of World War II, leaving her position as the math teacher at Robert Russa Moton High School in Farmville, VA to take what she believed would be a temporary war job. Two years after President Roosevelt signed Executive Order 8802 into law, prohibiting racial, religious and ethnic discrimination in the country's defense industry, the laboratory began hiring black women to meet the skyrocketing demand for processing aeronautical research data. Urgency and twenty-four hour shifts prevailed, as did Jim Crow laws which required newly-hired "colored" mathematicians to work separately from their white female counterparts. But...
... Vaughan was assigned to the segregated "West Area Computing" unit, an all-black group of female mathematicians, who were originally required to use separate dining and bathroom facilities. Over time, both individually and as a group, the West Computers distinguished themselves with contributions to virtually every area of research at Langley.
The group's original section heads (first Margery Hannah, then Blanche Sponsler) were white. In 1949, Dorothy Vaughan was promoted to lead the group, making her the NACA's first black supervisor, and one of the NACA's few female supervisors (see also Virginia Tucker). The Section Head title gave Dorothy rare center wide visibility, and she collaborated with other well-known computers like Vera Huckel and Sara Bullock on projects such as compiling a handbook for algebraic methods for calculating machines. Vaughan was a steadfast advocate for the women of West Computing, and even intervened on behalf of white computers in other groups who deserved promotions or pay raises. Engineers valued her recommendations as to the best "girls" for a particular project, and for challenging assignments they often requested that she personally handle the work.

In 1958, when the NACA made the transition to NASA, segregated facilities, including the West Computing office, were abolished. Dorothy Vaughan and many of the former West Computers joined the new Analysis and Computation Division (ACD), a racially and gender-integrated group on the frontier of electronic computing. Dorothy Vaughan became an expert FORTRAN programmer, and she also contributed to the Scout Launch Vehicle Program. Scout, an acronym for Solid Controlled Orbital Utility Test system, is a four-stage solid fuel satellite system capable of launching a 385-pound satellite into a 500-mile orbit. There have been 118 Scout launches, and its overall 96 percent success rate has earned a spot in the National Air and Space Museum.
Dorothy Vaughan retired from NASA in 1971. She sought, but never received, another management position at Langley. Her legacy lives on in the successful careers of notable West Computing alumni, including Mary Jackson, Katherine Johnson, Eunice Smith and Kathryn Peddrew, and the achievements of second-generation mathematicians and engineers such as Christine Darden.